Welding process strategies for the heated tool welding of high wall thicknesses
Authors: M. Sc. Fabian Friedrich, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Andreas Seefried
DOI: https://doi.org/10.53192/JP202403156
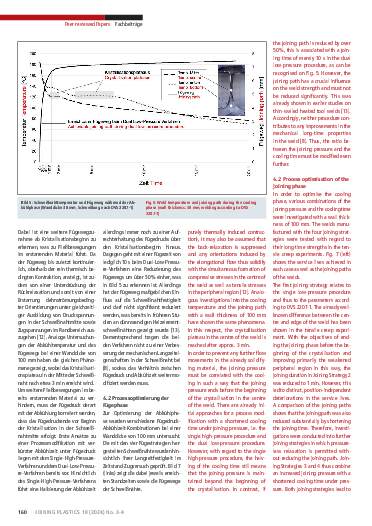
Although heated tool welding has been estabished for the joining of semi-finished products made of polyethylene for decades, investigations in the past have been restricted to wall thicknesses up to approx. 20 mm. However, large components with high wall thicknesses are frequently utilised also in order to extend the infrastructure for sustainable energy supply. In this respect, the parameters according to DVS 2207-1 are used in most cases. With high wall thicknesses, the extrapolated process times lead to long cooling phases under joining pressure and thus to substantial loads on the material during
the cooling. Complications in practice confirm the necessity of investigating alternative process strategies. Currently available alternatives (single high-pressure and dual low-pressure) do not lead to any better weld properties. In contrast, the tensile creep experiments carried out in an IGF project at the Chemnitz University of Technology show improved long-time behaviour due to the correlation of the end of the joining pressure with the beginning of the crystallisation in the weld.
An active subscription enables you to download articles or entire issues as PDF-files. If you already are a subscriber, please login. More information about the subscription